Crop Production (Rabi) : Makeup Solution by AGRI Grovestudies
Section A
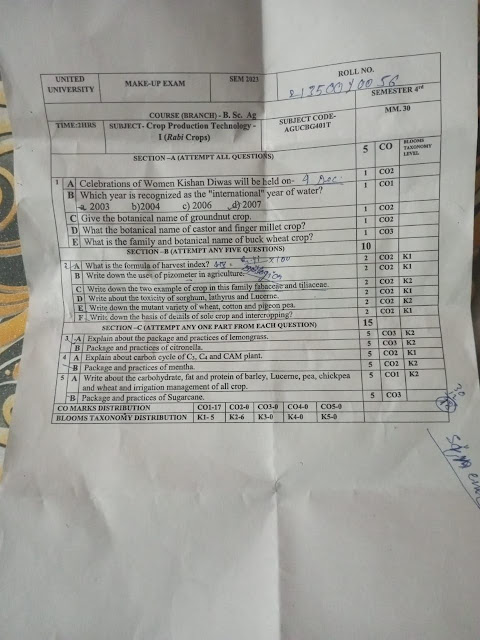
1a. 23 , December (Kisan Diwas )
1b. 2007 ( Int. water)
1c. Groundnut - Arachis hypogaea L.
1d. Finger millet - Eleusine coracana
Castor - Ricinus communis
1e. Botanical Name - Fagopyrum escultentum
Family - Polygonaceae
Section B
2a. The formula for Harvest Index (HI) is:
Harvest index = (Economic yield) / (biological yield)OR HI = (edible portion weight / total plant weight) x 100
Where:
- Edible portion weight: The weight of the part of the plant that is consumed by humans or animals.
- Total plant weight: The weight of the entire plant, including both edible and non-edible portions.
2b. A piezometer is an instrument used to measure the pressure of groundwater at a specific point in the soil. In agriculture, piezometers are used for the following purposes:
1. Irrigation management: Piezometers can be used to determine the water level in the soil and help farmers decide when to irrigate their crops.
2. Drainage system design: Piezometers can be used to determine the depth of the water table and help design drainage systems to prevent waterlogging.
3. Soil compaction management: Piezometers can be used to determine the effect of soil compaction on water movement and help farmers manage soil compaction.
4. Nutrient management: Piezometers can be used to determine the depth of the water table and help farmers manage nutrient leaching.
5. Environmental monitoring: Piezometers can be used to monitor groundwater levels and help assess the impact of agricultural practices on the environment.
2c. Two examples of crops in the family Fabaceae are peas and lentils and soyabean .
Two examples of crops in the family Tiliaceae are jute and ramie.
2d. Toxicity -
Sorghum - HCN , - Lathyrus - neurotoxin ,- Leucerne - Saponin
2e. Mutant variety -
Wheat - Sarbati , Sonara
Cotton - MCU - 7 , MCU - 10
Pigeon pea - Tombey , Vishakha - 1
2f. Sole crop refers to the practice of growing only one type of crop in a particular area. This is a common practice in modern agriculture, where large fields are typically planted with a single crop, such as corn or wheat. The advantages of sole cropping include the ability to optimize fertilizer and irrigation practices for a single crop, as well as the ease of harvesting and processing a uniform crop.
Intercropping, on the other hand, involves planting multiple crops together in the same field. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as planting different crops in alternating rows or planting them in the same row. Intercropping has several advantages, including increased biodiversity, reduced pest and disease pressure, and improved soil health. It can also help to maximize yields and reduce the risk of crop failure, as different crops may have different environmental requirements and may be more or less susceptible to certain pests and diseases. Some examples of intercropping include planting legumes (such as peas or beans) alongside corn or other cereal crops, or planting cover crops (such as clover or rye) alongside cash crops to improve soil health.